
| Online Judge | Online Exercise | Online Teaching | Online Contests | Exercise Author |
|
F.A.Q Hand In Hand Online Acmers |
Best Coder beta VIP | STD Contests DIY | Web-DIY beta |
k-edge connected components
Time Limit: 4000/2000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Submission(s): 227 Accepted Submission(s): 155
Problem Description
Efficiently computing k-edge connected components in a large graph G = (V, E), where V is the vertex set and E is the edge set, is a long standing research problem. It is not only fundamental in graph analysis but also crucial in graph search optimization algorithms. Computing k-edge connected components has many real applications. For example, in social networks, computing k-edge connected components can identify the closely related entities to provide useful information for social behavior mining. In a web-link based graph, a highly connected graph may be a group of web pages with a high commonality, which is useful for identifying the similarities among web pages. In computational biology, a highly connected subgraph is likely to be a functional cluster of genes for biologist to conduct the study of gene microarrays. Computing k-edge connected components also potentially contributes to many other technology developments such as graph visualization, robust detection of communication networks, community detection in a social network.
Clearly, if a graph G is not k-edge connected, there must be a set C of edges, namely a cut, such that the number |C| of edges in C is smaller than k and the removal of the edges in C cuts the graph G into two disconnected subgraphs G1 and G2. A connected component is a maximal connected subgraph of G. Note that each vertex belongs to exactly one connected component, as does each edge.
Now, we give you a undirected graph G with n vertices and m edges without self-loop or multiple edge, your task is just find out the number of k-edge connected components in G.
Clearly, if a graph G is not k-edge connected, there must be a set C of edges, namely a cut, such that the number |C| of edges in C is smaller than k and the removal of the edges in C cuts the graph G into two disconnected subgraphs G1 and G2. A connected component is a maximal connected subgraph of G. Note that each vertex belongs to exactly one connected component, as does each edge.
Now, we give you a undirected graph G with n vertices and m edges without self-loop or multiple edge, your task is just find out the number of k-edge connected components in G.
Input
Multicases. 3 integer numbers n, m and k are described in the first line of the testcase.(3¡Ün¡Ü100, 1¡Üm¡Ün¡Á(n-1)/2,2¡Ük¡Ün)The following m lines each line has 2 numbers u, v describe the edges of graph G.(1¡Üu,v¡Ün,u¡Ùv)
Output
A single line containing the answer to the problem.
Sample Input
5 6 3 1 3 2 3 1 4 2 4 1 5 2 5 9 11 2 1 2 1 3 2 3 4 5 4 6 5 6 7 8 7 9 8 9 1 4 1 7 16 30 3 1 2 1 3 1 4 2 3 2 4 3 4 5 6 5 7 5 8 6 7 6 8 7 8 9 10 9 11 9 12 10 11 10 12 11 12 13 14 13 15 13 16 14 15 14 16 15 16 1 5 2 6 1 9 2 10 1 13 2 14
Sample Output
5 3 4
Hint
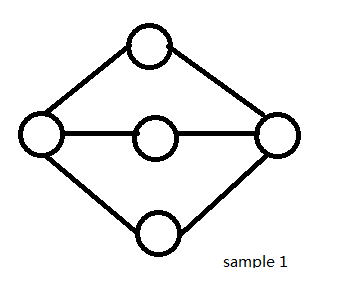
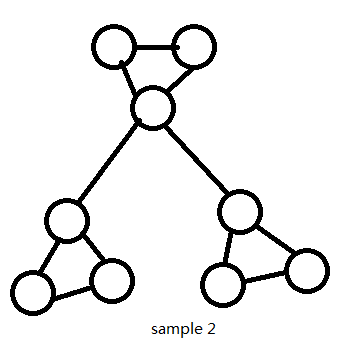
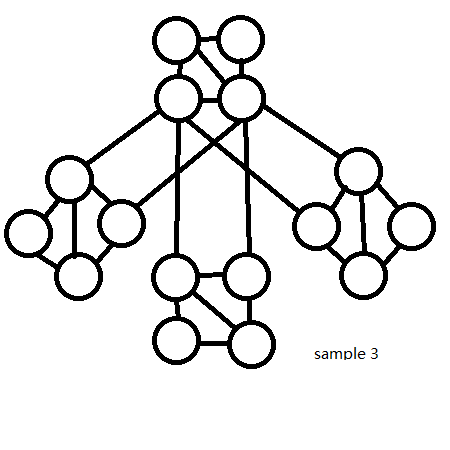
Source
| Home | Top |
Hangzhou Dianzi University Online Judge 3.0 Copyright © 2005-2024 HDU ACM Team. All Rights Reserved. Designer & Developer : Wang Rongtao LinLe GaoJie GanLu Total 0.000000(s) query 1, Server time : 2024-11-22 09:38:25, Gzip enabled |
Administration |