
| Online Judge | Online Exercise | Online Teaching | Online Contests | Exercise Author |
|
F.A.Q Hand In Hand Online Acmers |
Best Coder beta VIP | STD Contests DIY | Web-DIY beta |
Triangle
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Submission(s): 517 Accepted Submission(s): 298
Problem Description
A triangle is one of the basic shapes of geometry: a polygon with three corners or vertices and three sides or edges which are line segments.
Triangles can be classified according to the relative lengths of their sides:
· In an equilateral triangle all sides have the same length. An equilateral triangle is also a regular polygon with all angles measuring 60°.
· In an isosceles triangle, two sides are equal in length. An isosceles triangle also has two angles of the same measure; namely, the angles opposite to the two sides of the same length; this fact is the content of the Isosceles triangle theorem.
· In a scalene triangle, all sides are unequal. The three angles are also all different in measure. Some (but not all) scalene triangles are also right triangles.
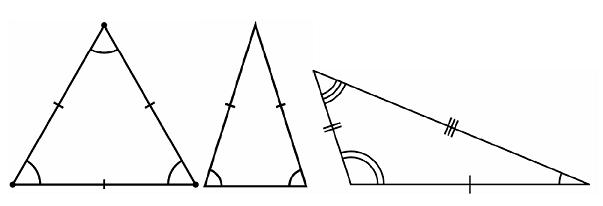
Triangles can be classified according to the relative lengths of their sides:
· In an equilateral triangle all sides have the same length. An equilateral triangle is also a regular polygon with all angles measuring 60°.
· In an isosceles triangle, two sides are equal in length. An isosceles triangle also has two angles of the same measure; namely, the angles opposite to the two sides of the same length; this fact is the content of the Isosceles triangle theorem.
· In a scalene triangle, all sides are unequal. The three angles are also all different in measure. Some (but not all) scalene triangles are also right triangles.

Input
The first line of input contains an integer (1 <= T <= 100), the number of test cases. T test data sets follow, each data set consists of 3 integers A, B and C, where (1 <= A,B,C <= 1,000,000) the triangle side lengths.
Output
For each test case, print “equilateral”, “isosceles” or “scalene” describing the triangle type. If the input doesn’t create a valid triangle output “invalid!”. Follow the output format below.
Sample Input
2 3 3 4 6 4 2
Sample Output
Case #1: isosceles Case #2: invalid!
Source
| Home | Top |
Hangzhou Dianzi University Online Judge 3.0 Copyright © 2005-2025 HDU ACM Team. All Rights Reserved. Designer & Developer : Wang Rongtao LinLe GaoJie GanLu Total 0.000000(s) query 1, Server time : 2025-04-01 08:40:42, Gzip enabled |
Administration |